Apoptosis Induction
Induction of Apoptosis
“Apoptosis” is a genetically programmed mechanism of cell death. When certain stimuli are applied to a cell, specific genes trigger a self-destruction mechanism, leading to cell death. Once apoptosis occurs, the DNA of cancer cells becomes fragmented and eventually disappears.
Verification of apoptosis effect
A study was conducted on the influence of mozuku (Cladosiphon okamuranus) derived fucoidan, kombu (Laminaria japonica) derived fucoidan, and agaricus mycelium extract powder on apoptosis in promyelocytic leukemia cell lines (HL60) and cultured human ovarian tumor cell lines (NOS4).
・Experimental Method
Applied mozuku (Cladosiphon Okamuranus) derived fucoidan, kombu (Laminaria japonica) derived fucoidan and agaricus mycelium extract powder onto each promyelocytic leukemia cell strain (HL60) and cultured human ovarian tumor cell strains (NOS4) and cultured them.
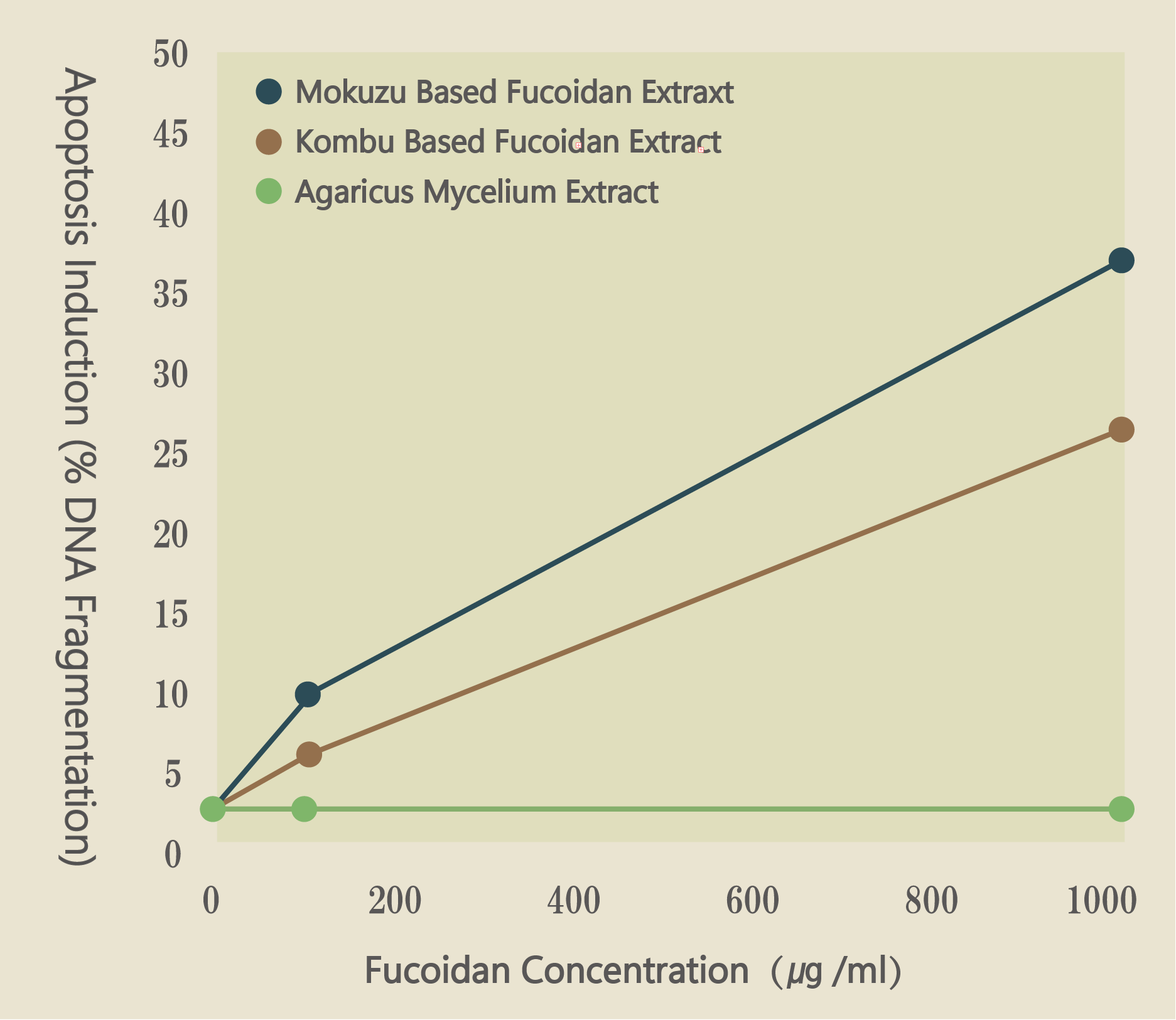
Apoptosis Induction to Promyelocytic Cell Strain(HL60)
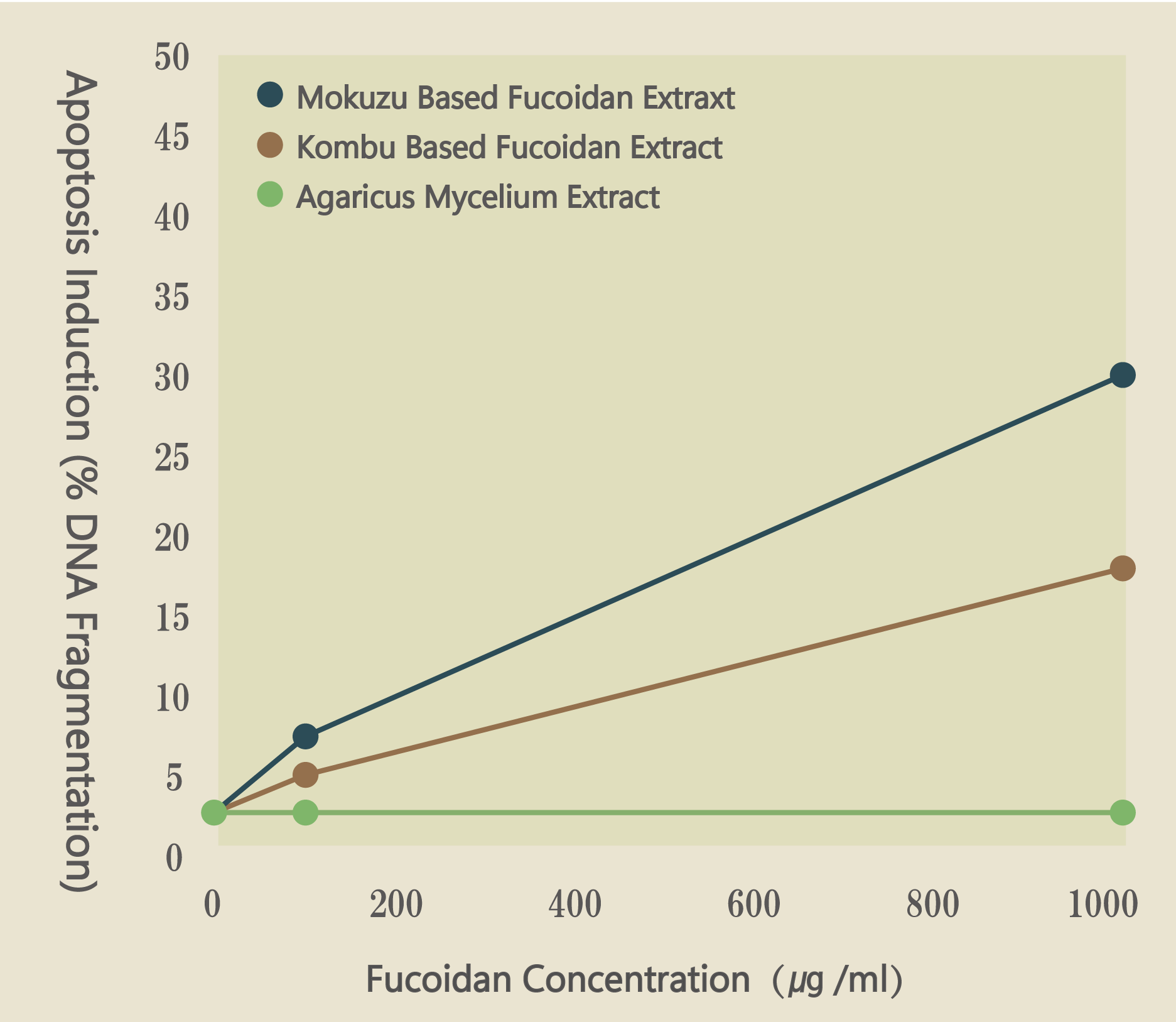
Apoptosis Induction to Human Ovarian Tumor Cell (NOS4)
(12th International Congress of Immunology)
Effects of each type of fucoidan and agaricus inducing apoptosis
When agaricus was applied to the cancer cell, there was no apoptosis effect. The results did reveal that mozuku derived fucoidan and kombu derived fucoidan exhibited a high ability to induce apoptosis.
Verification of apoptosis induction ability
We examined the effect of mozuku-derived fucoidan on the induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7).
・Experimental Method
Mozuku derived fucoidan (sample ①) and mozuku derived fucoidan prepared with a caspase-7 inhibitor (sample ②) were each added to cultures of MCF-7 cells. As a control (sample ③), no additives were introduced to the culture. The cells were then incubated under standard conditions. (See Illustration 1)
We also examined the activation of caspase-7 after it was added to fucoidan. (See Illustration 2)
Caspase…Caspase-7 is an apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase and a member of the caspase (cysteine-aspartate protease) family. It is known to function as an executioner protein in the apoptotic process. The sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution phase of apoptosis.
Caspases are initially synthesized as inactive proenzymes and become activated through proteolytic cleavage by upstream caspases (e.g., caspase-8 and caspase-9) at conserved aspartic acid residues. This cleavage produces two subunits—large and small—which dimerize to form the active heterotetrameric enzyme.
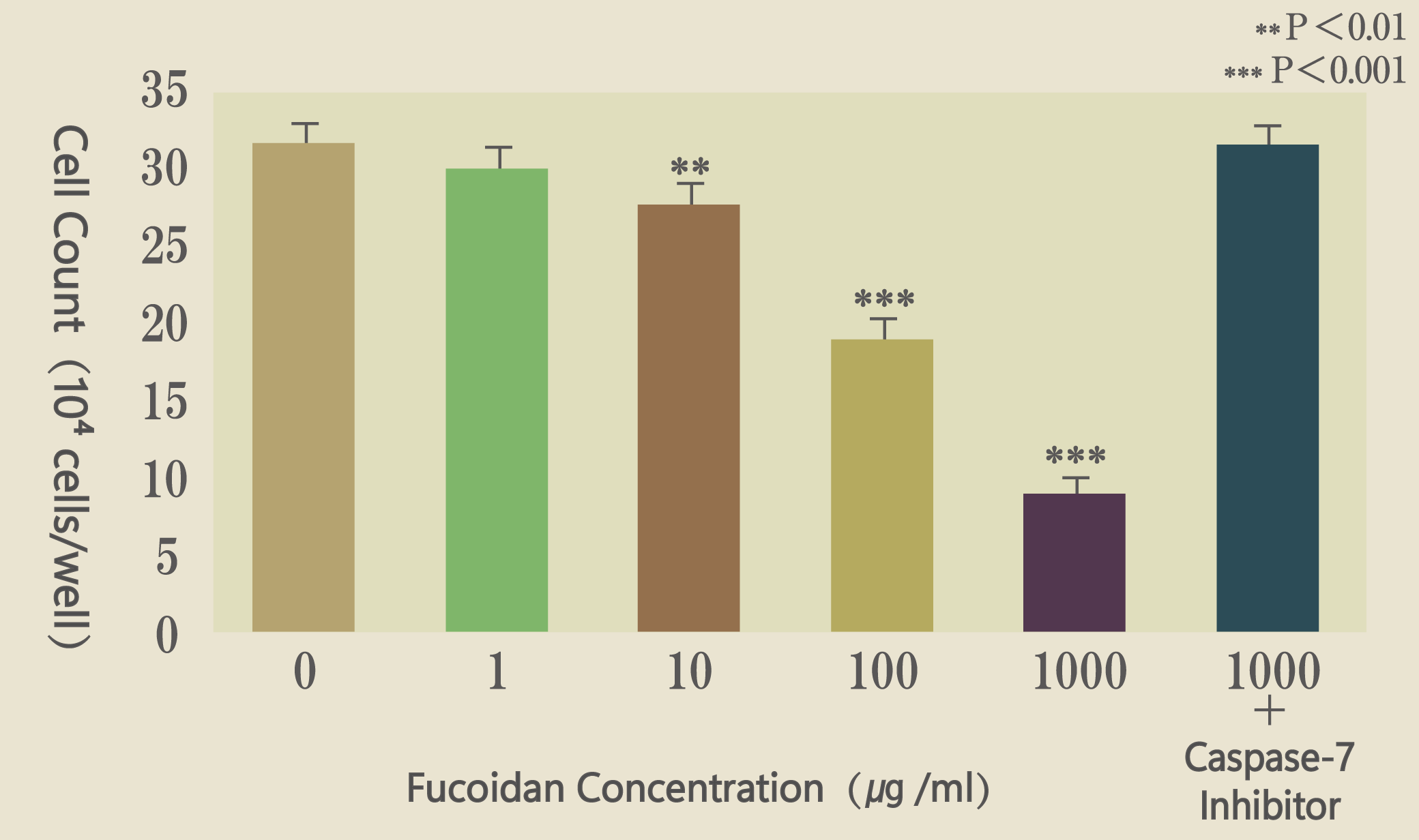
Suppression of MCF-7 Cell Growth (Illustration 1)
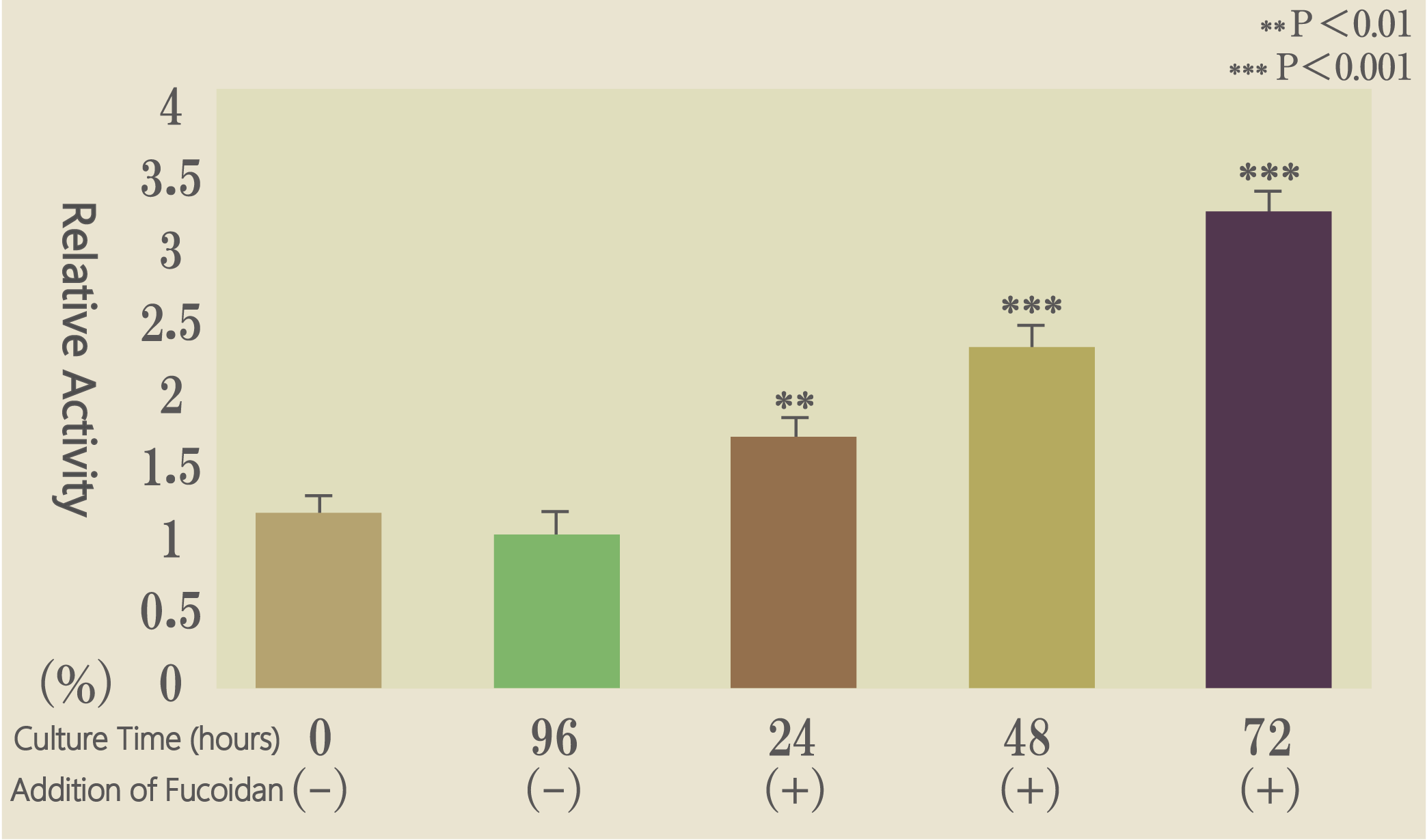
Caspase-7 (Illustration 2)
Effects of mozuku derived fucoidan on apoptosis induction
When fucoidan was applied to cancer cells, the density of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) decreased, indicating a loss of density-dependent growth. Treatment with 1000 μg of fucoidan resulted in a reduction in cancer cell numbers. However, when 1000 μg of fucoidan was administered together with a caspase-7 inhibitor, no significant change in cell number was observed. (See Illustration 1)
These results suggest that mozuku derived fucoidan induces apoptosis through the activation of caspase-7. To confirm this, we measured caspase-7 activity and found that it was indeed activated by fucoidan treatment. (See Illustration 2)
We are conducting research on fucoidan, whose various physiological functions have been elucidated, including 'anti-tumor,' 'cholesterol-lowering,' 'blood pressure-lowering,' and 'anti-virus' effects.
